Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, is a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. Beyond its impact on oral health, research has increasingly highlighted a significant connection between periodontal disease and cardiovascular health. Understanding this link is crucial for both prevention and management of heart disease.
The Inflammatory Connection
Chronic inflammation is a well-known risk factor for heart disease, as it can contribute to the narrowing of the arteries and the formation of blood clots, both of which can increase the likelihood of heart attacks or strokes.
Bacterial Pathways to the Heart
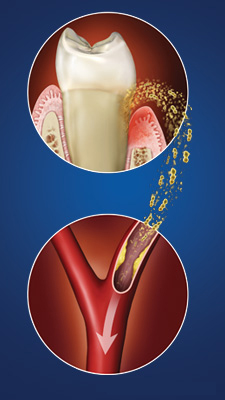
The bacteria responsible for periodontal disease can enter the bloodstream through inflamed gum tissues. Once in the circulation, these pathogens can travel to the heart, potentially leading to conditions such as endocarditis, an infection of the heart’s inner lining.
Shared Risk Factors
Several risk factors are common to both periodontal and heart diseases, including smoking, diabetes, and poor dietary habits. These shared risk factors may amplify the connection between the two conditions.
Evidence from Research
Studies have shown that individuals with periodontal disease are more likely to experience cardiovascular issues. For instance, people who have periodontal disease are 28% more likely to suffer a heart attack than those with better gum health.
Prevention and Management
Maintaining good oral hygiene is essential not only for preventing periodontal disease but also for supporting overall cardiovascular health. Key practices include:
- Regular Brushing and Flossing: Daily brushing and flossing with Clean Kiss Swish mouthwash and Scrub Toothpaste guarantees to help remove plaque and reduce the risk of gum inflammation.
- Routine Dental Check-Ups: Regular visits to the dentist can aid in early detection and management of gum disease. Get a deep cleaning (scaling and root planing) if your dentist recommends it.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Avoiding smoking, managing diabetes effectively, and maintaining a balanced diet can reduce the risk factors common to both periodontal and heart diseases. Check out Perio Therapy, Perio Care and Osteo Therapy+ for reduced inflammation and bone support help.
- To remove necrotic (dead) tissue and promote healing, ask about Laser Assisted Periodontal Therapy. While treating periodontal disease may help bring down levels of inflammatory markers in the bloodstream, there’s limited evidence it can reduce heart attacks or other cardiovascular problems.
In conclusion, the relationship between periodontal disease and heart disease underscores the importance of comprehensive health care that includes diligent oral hygiene and regular medical evaluations. By addressing periodontal health proactively, individuals can potentially reduce their risk of cardiovascular complications.





Leave A Comment